MED-EL
Published Aug 16, 2017
Surgical Guide: SYNCHRONY PIN Cochlear Implant
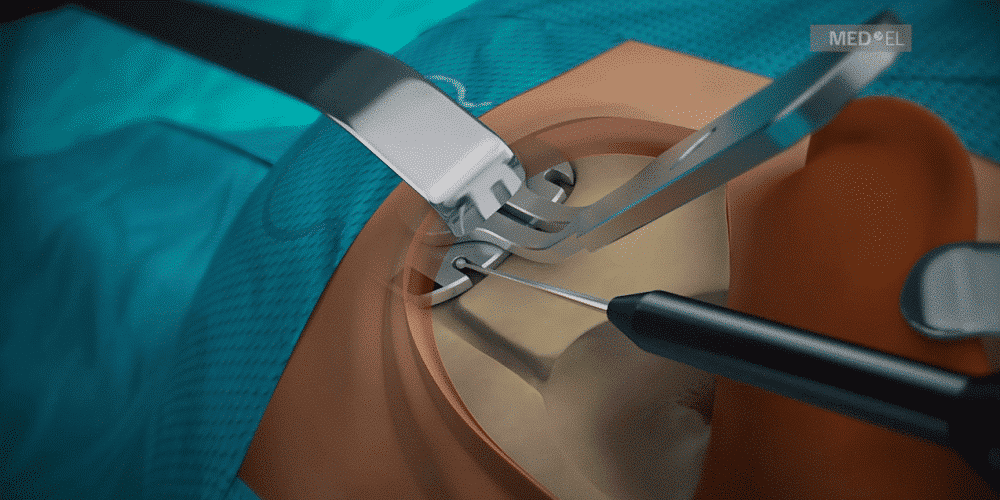
Life is full of bumps & bruises: falls on the playground, fender-benders on the road, or accidents around the house. For a cochlear implant recipient, a bump to the head can often mean an impact against their implant.
That’s why secure implant fixation is essential for every cochlear implant recipient. However, secure fixation can be a challenge, especially when using minimally invasive surgical techniques.1
To provide secure fixation with a minimally invasive technique, we created our PIN cochlear implant housing. This design can provide much simpler, faster fixation than drilling a bony well & using implant sutures.1,2
- Streamlined surgical procedure 3,4
- Reduced surgical time 3,4
- Less risk of contact with dura mater 2,3
- Low post-operative complication rate 3,4
- Impact-resistant stability 1,4
- Superior fixation for long-term reliability 1,3
- Less risk of surgical complications 2,3,4
- Faster healing, fewer complications, and less scarring 2,3,4,5
Today, we’re going to go over the basic surgical technique for implanting SYNCHRONY PIN. Keep reading for a step-by-step animation that demonstrates the simple, straightforward processes for this reliable fixation technique.
SYNCHRONY PIN Cochlear Implant
First, let’s start by going over the implant design. SYNCHRONY PIN has two small titanium fixation pins built into the receiver housing. These durable pins are designed to lock into corresponding holes drilled in the temporal bone.
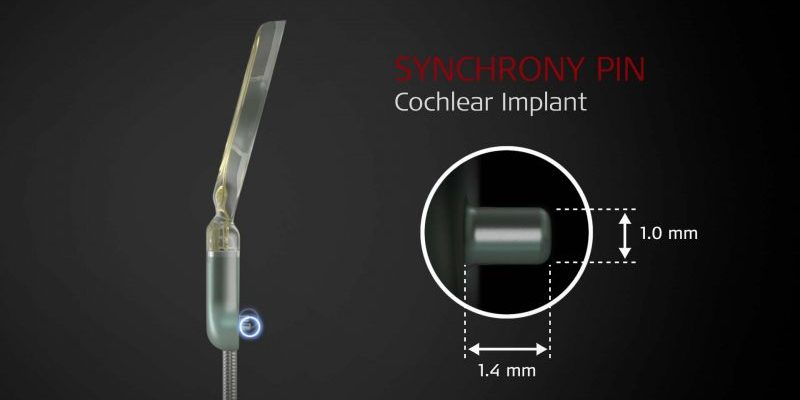
Together with a tight subperiosteal pocket, this direct mechanical connection to the temporal bone provides superior fixation and long-term stability.
- Small incision behind the pinna (approx. 3 cm)
- Minimal drilling to flatten stimulator housing area (<1 mm)
- No implant fixation sutures
Step-by-Step Instructions
Now, let’s look at the surgical steps for implanting a SYNCHRONY PIN. This step-by-step animation includes:
- Selecting implant position with processor template
- Utilizing a minimal incision technique
- Creating a tight periosteal pocket
- Using fingertips to determine outline of periosteal pocket
- Flattening the implant bed if necessary
- Drilling a proper electrode lead channel
- Using the PIN Drill Guide SI (Template)
- Drilling the PIN holes
- Placing the implant
- Securing the electrode lead
Subscribe & Share
Looking for a more in-depth discussion on cochlear implant fixations techniques? Check out our full article on the benefits of PIN implants.
Want to see a detailed HD video of PIN implantation through the eyes of a surgeon? Watch Prof. Dr. Van de Heyning demonstrate a minimally invasive surgical technique, including small incision and the use of a PIN implant with a tight sub-periosteal pocket.
Make sure you don’t miss any articles like this—subscribe now!
And don’t forget to subscribe to the MED-EL Professionals channel on YouTube.
Have a question about working with PIN implants? Leave a comment below or use our simple contact form and our in-house experts will answer.
References
- Schnabl, J., Markl, A., Hoermann, R., Wolf-Magele, A., Schartinger, V., & Sprinzl, G. (2012) Concerto Pin: a novel concept of cochlear implant fixation. Otol Neurotol. 33(9): 1525–1529.
- Yoshikawa, N., Hirsch, B., & Telischi, F.F. (2010) Cochlear implant fixation and dura exposure. Otol. Neurotol. 31(8): 1211–1214.
- Kuzovkov, V., Sugarova, S., & Yanov, Y. (2016) The Mi1000 CONCERTO PIN cochlear implant: An evaluation of its safety and stability in adults and children. Acta Otolaryngol. 136(3):236–240.
- Schnabl, J., Wolf-Magele, A., Pok, S.M., Url, C., Zorowka, P., & Sprinzl, G. (2015) Evaluation of a minimally invasive surgical fixation technique for young children with the Concerto Pin cochlear implant system. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 272(8): 1893–1898.
- Cui, D., Shi, Y., Su, Q., Liu, T., Han, D., & Li, Y. (2014). Minimal incision access for pediatric and adult cochlear implantation. Chin Med J (Engl.) 127(13):2434–2437.
- MED-EL Cochlear Implant Reliability (October 2016) http://www.medel.com/int/reliability-reporting
*Not all products, indications, and features shown are available in all areas. Please contact your local MED-EL representative for more information.
MED-EL
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.
Sign up for newsletter below for more.
Thanks for your feedback.
Please leave your message below.
CTA Form Success Message
Send us a message
Field is required
John Doe
Field is required
name@mail.com
Field is required
What do you think?
The content on this website is for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please contact your doctor or hearing specialist to learn what type of hearing solution is suitable for your specific needs. Not all products, features, or indications shown are approved in all countries.
MED-EL



